Fibreglass reinforced plastic (FRP) tanks are widely used across industrial operations for their corrosion resistance, strength, and long service life. However, even durable storage systems require routine cleaning and inspection to maintain safety and performance over time.
Without regular maintenance, residue buildup, structural wear, or contamination can develop inside the tank. These issues reduce efficiency and increase the risk of failure. The listicle below outlines the essential steps industries follow to clean and inspect FRP tanks for long-term use safely.
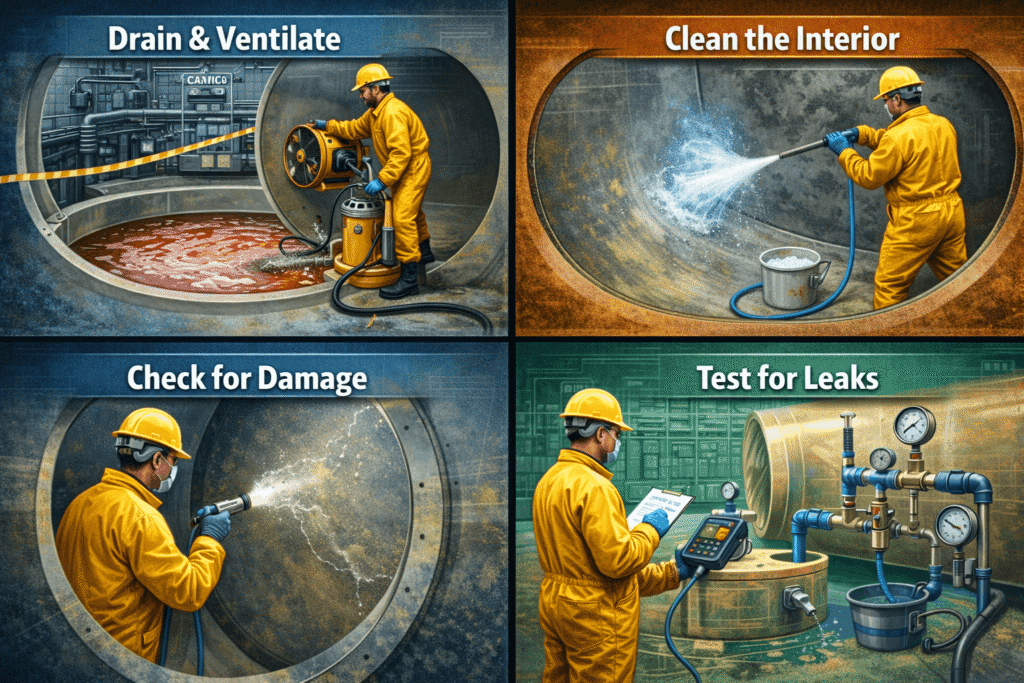
1. Prepare the FRP Storage Tank and Work Area
Safe maintenance begins before any cleaning. Proper preparation protects personnel and prevents accidental damage to the tank.
Key preparation steps include:
- Draining and isolating the tank by removing all contents and closing valves
- Ventilating the workspace to prevent the buildup of fumes
- Wearing appropriate protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and respirators
- Reviewing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) to confirm cleaning agent compatibility with the tank’s resin system
Thorough preparation reduces hazards and helps preserve the internal tank surface.
2. Rinse and Remove Residue from FRP Tanks
Once access is safe, begin cleaning with a controlled rinse. This step removes loose deposits and prepares the surface for inspection.
Best practices include:
- Using clean water at low pressure to avoid damaging the lining
- Applying non-abrasive brushes and mild, approved cleaning solutions for heavier buildup
- Avoid using metal tools or scrapers that may scratch the resin
- Rinse multiple times to remove cleaning agents fully
- Checking drain and vent lines for unrestricted flow
A properly cleaned surface is essential for identifying defects during inspection.
3. Inspect Internal and External FRP Tank Surfaces
After the tank has dried, conduct a detailed visual inspection. Focus on areas exposed to stress, chemicals, or environmental conditions.
Internal inspection checklist
- Blisters, cracks, or delamination in the resin
- Discolouration or softening resulting from chemical exposure
- Integrity of seams, joints, and bonded connections
External inspection checklist
- Abrasions, UV damage, or exposed fibres
- Condition of supports, ladders, and fittings
- Wear on gaskets and sealing materials
Document any defects immediately and review them with maintenance or engineering teams before returning the tank to service.
4. Evaluate Structural Integrity of FRP Water Storage Tanks
Visual inspections should be supported by periodic non-destructive testing to confirm mechanical performance.
Common evaluation methods include:
- Ultrasonic thickness testing to check wall uniformity
- Acoustic emission testing to detect micro-cracks under stress
- Hydrostatic pressure testing to confirm leak resistance after repairs
These assessments help verify that the tank continues to meet its design requirements.
5. Apply Protective Measures to Extend Tank Life
After cleaning and inspection, protective actions help preserve long-term reliability.
Recommended measures include:
- Reapplying UV-resistant coatings to exposed surfaces
- Replacing worn gaskets, fittings, or seals
- Maintaining corrosion-resistant linings for aggressive media
- Recording all maintenance activities in service logs
Routine renewal of coatings and seals supports consistent performance in demanding industrial environments.
6. Establish a Maintenance Schedule for FRP Tanks
Consistency is critical for long-term service. Cleaning and inspection frequency should reflect tank usage, stored materials, and environmental exposure.
General guidelines include:
- Annual inspections for standard water storage
- More frequent checks for chemical storage or high-temperature applications
A structured maintenance schedule reduces repair costs and supports compliance with industry standards.
Supporting Safe, Efficient Operations
FRP storage tanks play a critical role in industrial water and chemical handling. With routine cleaning, inspection, and testing, these systems deliver reliable performance year after year.
Following a structured maintenance process helps prevent corrosion, contamination, and structural failure.