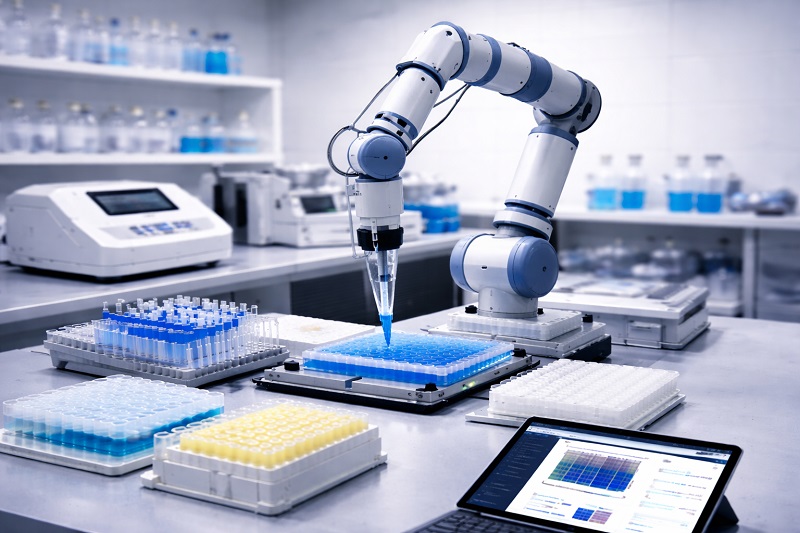
Biotech laboratories are no longer built around isolated instruments or single-purpose workstations. Today’s facilities are shared environments where multiple teams, workflows, and instruments must operate in parallel. As space constraints grow and throughput expectations increase, labs are turning to robotics that can adapt to changing demands rather than lock workflows into rigid configurations.
This shift has accelerated the adoption of the flexible robotic arm in modern biotech labs. Unlike fixed automation systems, flexible arms support shared lab spaces by moving between instruments, handling different tasks, and adjusting workflows without major reconfiguration. We see flexible robotics becoming a core component of labs that want to scale automation while preserving agility.
By integrating adaptable robotics with scheduling and orchestration software, biotech teams can reduce manual handling, improve consistency, and keep shared environments running efficiently—even as research priorities evolve.
Benefits of Flexible Robotic Arms
The primary advantage of a flexible robotic arm is versatility. These systems are designed to perform a wide range of tasks using the same hardware footprint, making them ideal for labs where workflows change frequently.
Key benefits include:
- Space efficiency: One robotic arm can service multiple instruments, reducing the need for dedicated automation cells.
- Workflow adaptability: Arms can be reprogrammed to support new assays, devices, or protocols without physical redesign.
- Improved utilization: Instead of idle automation, flexible arms stay productive by moving between tasks.
- Reduced manual handling: Automating transfers lowers the risk of errors, contamination, and repetitive strain.
For biotech labs balancing exploratory research with high-throughput operations, flexibility is often more valuable than raw speed. Rather than committing to single-purpose robots, teams can deploy adaptable arms that evolve alongside their research pipelines.
How Collaborative Robotic Arms Support Complex Workflows
A collaborative robotic arm is specifically designed to operate safely alongside people and other automation systems. In biotech labs, this collaborative capability is critical—scientists, instruments, and robots often share the same physical space.
Collaborative arms support complex workflows by:
- Operating with built-in safety sensors that detect proximity
- Allowing direct human interaction during setup or intervention
- Enabling fast redeployment across different workstations
- Supporting fine-grained, repeatable movements for sensitive tasks
In practice, collaborative arms excel at bridging gaps between instruments. Rather than automating a single step, they connect workflows end to end—moving plates from incubators to readers, transferring samples between devices, and coordinating actions across multiple systems.
We design automation strategies in which collaborative robotics complements—not replaces — scientists. By handling repetitive transfers and timing-sensitive actions, these arms free researchers to focus on experimental design, troubleshooting, and analysis.
Use Cases in Biotech: Sample Transfer and Device Loading
Flexible and collaborative robotic arms are especially effective in workflows where coordination matters more than raw throughput. Common biotech use cases include:
Sample Transfer
Sample movement between instruments is one of the most frequent and error-prone manual tasks in biotech labs. Robotic arms automate these transfers with precision and repeatability.
Examples include:
- Moving plates between incubators, readers, and washers
- Transferring samples from preparation stations to analysis devices
- Coordinating handoffs between liquid handlers and downstream instruments
By automating transfers, labs reduce timing variability and ensure that samples are processed consistently across experiments.
Device Loading and Unloading
Many instruments require frequent loading and unloading, creating natural bottlenecks. Flexible robotic arms keep devices running continuously by automatically managing these tasks.
This includes:
- Loading plates into readers or imagers
- Removing completed runs and staging the next batch
- Supporting overnight or unattended operation
These use cases demonstrate why robotics is no longer limited to large, fixed automation cells. Flexible arms allow labs to automate selectively—targeting high-impact tasks without redesigning entire workflows.
Integration With Scheduling and Automation Software
Robotic arms deliver the most value when they are part of a coordinated automation ecosystem. Without orchestration, even the most advanced robot becomes another isolated tool.
Companies focus on integrating robotic arms directly with scheduling and automation software so tasks are coordinated dynamically rather than executed in isolation. When connected to orchestration platforms:
- Robotic actions align with instrument availability
- Transfers occur at the optimal time, not just the next available slot
- Workflows adapt automatically when steps finish early or late
- Idle time across instruments is reduced
This integration turns a flexible robotic arm into an intelligent workflow component rather than a standalone device.
Our approach ensures that robotic arms communicate with incubators, readers, liquid handlers, and data systems as part of a unified process. The result is smoother execution, higher utilization, and fewer manual interventions across the lab.
Why Flexible Robotics Matters for the Future of Biotech Labs
As biotech research becomes more interdisciplinary and collaborative, labs need automation that supports change—not resists it. Fixed systems may deliver speed in narrow use cases, but they struggle when workflows shift or new instruments are introduced.
Flexible and collaborative robotic arms offer a future-ready alternative by:
- Supporting incremental automation strategies
- Adapting to new workflows without hardware replacement
- Enabling shared lab environments to scale efficiently
- Integrating cleanly with orchestration and scheduling platforms
We help biotech teams deploy robotic solutions that grow with them. By pairing adaptable robotics with intelligent scheduling software, we enable labs to automate strategically—without sacrificing flexibility or control.
Conclusion
The modern biotech workflow demands automation that is adaptable, integrated, and collaborative. A flexible robotic arm plays a critical role in meeting these demands by connecting instruments, supporting shared spaces, and reducing manual intervention.
When paired with orchestration software, a collaborative robotic arm becomes more than a mechanical tool—it becomes a central contributor to efficient, scalable workflows.
We work with biotech labs to integrate flexible robotics into automation strategies that support today’s research and tomorrow’s growth.